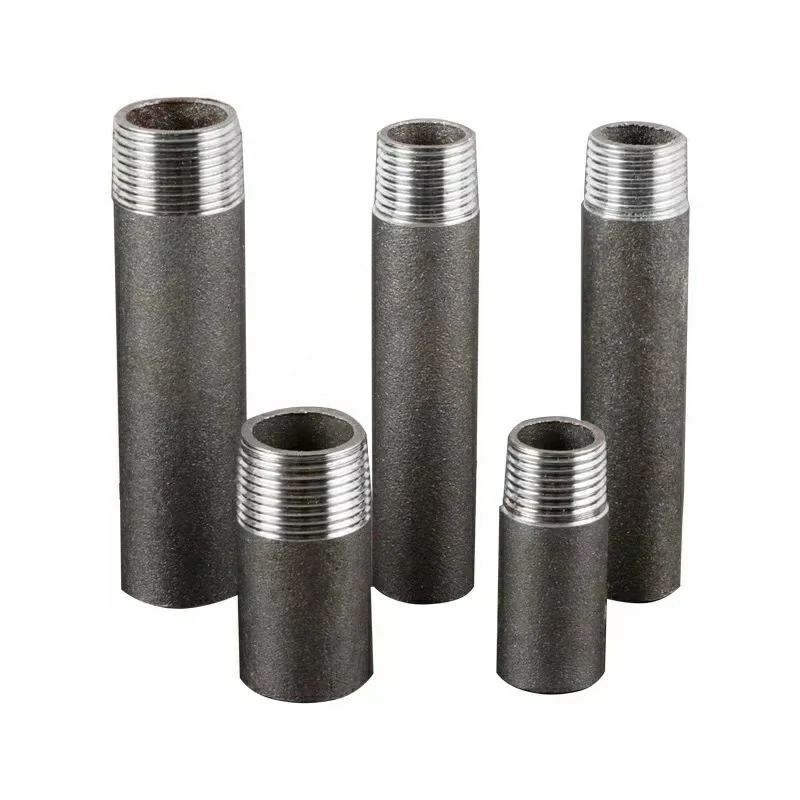
The types of threads commonly used for the threaded end of pipe nipples depend on the industry standards and specific applications. Two of the most prevalent thread types used for pipe nipples are NPT (National Pipe Thread) and BSP (British Standard Pipe).
Here’s an overview of these thread types:
- NPT (National Pipe Thread):
- NPT threads are one of the most widely used thread standards in the United States for pipe fittings and connections.
- NPT threads have a tapered design, which means the diameter of the threads decreases along the length of the pipe nipple.
- They are available in both NPT and NPTF (National Pipe Taper Fuel) variations. NPTF threads are designed for applications where a leak-tight seal is critical.
- NPT threads are suitable for both gas and liquid applications, making them versatile for a wide range of industries.
- BSP (British Standard Pipe):
- BSP threads are commonly used in the United Kingdom and other parts of the world adhering to British standards.
- Unlike NPT threads, BSP threads have a parallel design, which means the diameter remains consistent along the length of the pipe nipple.
- The two most common variations are BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel) and BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered). BSPP threads are parallel, while BSPT threads are tapered.
- BSP threads are often used for water and gas applications, as well as pneumatic systems.
It’s essential to choose the appropriate thread type for your specific application, as the compatibility of threads is crucial to ensure a leak-tight connection. Using the wrong thread type can lead to leaks, improper sealing, and potential system failures.
When selecting pipe nipples, it’s also important to consider the intended use, industry standards, and local regulations, as these factors may influence the choice of thread type. Always follow the recommended thread standards and use proper sealing methods, pipe nipple threaded one end such as thread sealant or tape, to ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
How do you determine the appropriate size and length of a threaded one-end pipe nipple for a specific application?
Selecting the appropriate size and length of a threaded one-end pipe nipple for a specific application is crucial to ensure a well-functioning and leak-free plumbing or piping system. To make the right choice, consider the following steps:
- Understand the Application:
- First, understand the purpose and requirements of your specific application. Determine the type of fluid (liquid or gas) being conveyed, the pressure and temperature conditions, and any specific regulations or standards that apply.
- Size Selection:
- Choose the appropriate pipe nipple size. The size should match the size of the existing pipe or the equipment to which the nipple will be connected. The nominal pipe size (NPS) must be consistent to ensure proper flow and compatibility with other components.
- Length Selection:
- Measure the required length of the pipe nipple. Consider the distance between the connection points or the depth to which the nipple needs to extend into the equipment. You may need to use a measuring tool or tape to determine the required length accurately.
- Thread Type and End Configuration:
- Confirm the type of threads needed for your application. Select NPT or BSP threads, as appropriate, to ensure compatibility with the existing connections.
- Consider whether you need a nipple with one threaded end and one unthreaded end (the “one-end” threading configuration) to meet your specific requirements.
- Material Selection:
- Choose the appropriate material for the pipe nipple based on the fluid being conveyed and the environmental conditions. Common materials include black malleable iron, brass, stainless steel, or PVC. Ensure that the material is compatible with the fluid and the system.
- Pressure and Temperature Considerations:
- Check the pressure and temperature ratings of the pipe nipple material to ensure it can safely handle the conditions of your application. The fitting should be rated for the highest expected pressure and temperature.
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Verify that the selected pipe nipple and its material meet any industry-specific standards or regulations, especially if your application involves potable water or gas distribution, where compliance is critical.
- Leak Prevention:
- To ensure a leak-free connection, apply an appropriate thread sealant (e.g., Teflon tape or pipe thread compound) to the threads of the nipple before installation. Proper sealing helps prevent leaks at the connection points.
- Installation and Inspection:
- Follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions, which may include torque or tightening recommendations. Use the necessary tools to install the nipple securely, avoiding over-tightening, which can damage the threads.
- Testing and Monitoring:
- After installation, conduct a pressure or leakage test to ensure the system is functioning correctly. Monitor the system periodically for any signs of leaks or issues.
By following these steps and taking into account the specific requirements of your application, you can choose the appropriate size and length of a threaded one-end pipe nipple and ensure a reliable and leak-free connection in your plumbing or piping system. If you have any doubts or specific concerns, it’s advisable to consult with a professional plumber or piping expert for guidance.